Ever wondered how websites, apps, and tools manage tons of data so smoothly? The secret often lies in SQL — Structured Query Language.
Whether you’re building a website, analyzing sales data, or automating business reports, learning to simplify SQL can help you unlock the power of your data.
In this guide, you’ll discover what SQL is, how it works, and why it’s still one of the most in-demand data tools in today’s digital economy.
You’ll also find tips, examples, and FAQs throughout the article to help you understand and apply SQL with confidence.
👉 Learn more about data-powered tools at Microapp.
What is SQL?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language, a system that allows you to communicate with databases, much like a translator between you and your data.
IBM first developed it in the 1970s and has since become the industry standard for data management. Today, SQL is used across nearly every field, from finance and marketing to e-commerce and software development.
💡 Tip: If you’re managing structured content or analytics, explore A Beginner’s Guide to Structured Content to see how clear data structure boosts consistency and performance.
Or as an aspiring developer, learning SQL opens doors to smarter decisions, automation, and growth.
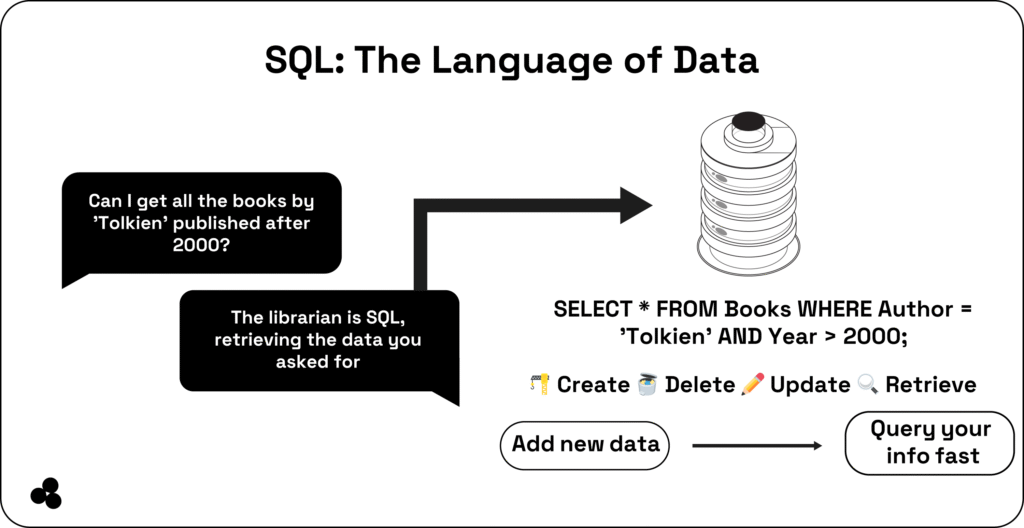
How SQL Works (Simplified for Beginners)
Think of SQL as the language that helps you interact with your database.
Data is stored in tables (rows and columns), similar to Excel sheets. SQL lets you query those tables using commands like SELECT, INSERT, or UPDATE to get exactly what you need.
Example:
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Country = 'USA';
This command tells the database: “Show me all customers from the USA.” 🇺🇸
💬 Is SQL considered a programming language or just a query tool? Technically, SQL is a domain-specific programming language — it’s designed to query and manage data, not build applications.
💡 Tip: Want to test your skills? Try DataCamp’s SQL Certification — it’s a great place to start learning hands-on.
👉 Learn how structured planning applies to data by checking out What Is Project Planning?.
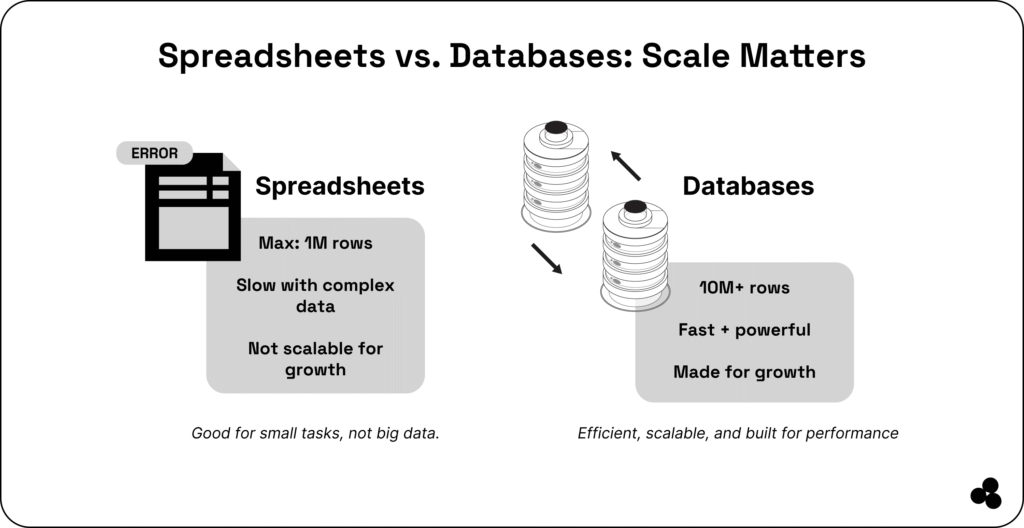
Why SQL Is So Popular
According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey, SQL consistently ranks among the top five most widely used technologies worldwide.
Why? Because it’s powerful, flexible, and integrates with almost every other programming language — from Python to JavaScript.
Marketers use SQL to filter campaign data, while finance teams use it for profit analysis. Even email automation systems rely on SQL for user segmentation — as explained in our Best Email Marketing Tools guide.
💬 Why do most companies still rely on SQL today? SQL remains vital because it’s simple, standardized, and works across nearly all database systems — cloud or on-premise.
Core SQL Commands (With Real Examples)
Here are some of the most common SQL commands you’ll use daily:
SELECT — Retrieve Data
SELECT name, email FROM users WHERE active = 1;
✏️ Use this to fetch specific user or product data from your database.
INSERT — Add Data
INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ('Ava', 'ava@email.com');
✏️ Use this when registering a new customer or adding an order record.
UPDATE — Modify Data
UPDATE users SET active = 0 WHERE last_login < '2024-01-01';
✏️ Perfect for bulk changes or keeping your customer data clean.
DELETE — Remove Data
DELETE FROM users WHERE inactive = 1;
⚠️ Be careful — once deleted, it’s gone for good.
👉 Related Reading: What Is a Good Profit Margin? See how SQL supports real-time financial tracking and reporting.
Types of SQL Commands (and When to Use Them)
SQL commands are grouped into five main categories, each with its own purpose.
| Type | Description | Example | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDL (Data Definition Language) | Defines the structure of a database | CREATE TABLE employees (id INT, name TEXT); | When setting up a new data system |
| DML (Data Manipulation Language) | Manages data records | INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE | For daily operations or CRM updates |
| DCL (Data Control Language) | Controls access permissions | GRANT, REVOKE | When setting user roles or security |
| TCL (Transaction Control Language) | Manages transactions | COMMIT, ROLLBACK | To undo or confirm large data changes |
| DQL (Data Query Language) | Focused on querying | SELECT * FROM users; | To extract reports or insights |
💡 Tip: Use Microapp’s SQL Escape/Unescape Tool to clean up data safely before importing or exporting between systems.
💬 What’s the difference between SELECT and JOIN in SQL? SELECT retrieves data from a single table, while JOIN combines data from multiple related tables.
Real-World Uses of SQL
SQL is everywhere, powering systems that keep businesses and daily life running smoothly.
Here’s where you’ll find it in action:
- Banking systems — managing transactions and accounts
- E-commerce — tracking sales, customers, and inventory
- Analytics dashboards — turning data into insights
- Email marketing — segmenting audiences and tracking engagement
- Finance and accounting apps — calculating profits and invoices (What Is an Invoice?)
👉 Related: Learn financial applications of data in the Budget Planner App.
SQL vs NoSQL — What’s the Difference?
| Feature | SQL | NoSQL |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured (tables) | Unstructured (documents, key-value) |
| Schema | Fixed | Flexible |
| Ideal For | Finance, CRMs, ERP | Big data, social networks |
| Example | MySQL, PostgreSQL | MongoDB, Firebase |
💡 Tip: Use SQL when your data is structured, predictable, and needs accuracy. Choose NoSQL when dealing with varied or fast-changing data types.
Getting Started with SQL
You don’t need a complex setup to learn SQL. Start with free tools like:
- MySQL Workbench
- SQLite Browser
- SQLFiddle or W3Schools SQL Editor
Then, consider taking a certification course or practicing challenges.
👉 Try the DataCamp SQL Associate program to build your credentials.
💬 How long does it take to learn SQL for beginners? With consistent practice, most people grasp the basics of SQL in 2–4 weeks.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Missing semicolons (
;) – They tell the system where one command ends. - Using WHERE incorrectly – Use it for filtering data;
HAVINGworks with groups. - Not normalizing data – Avoid duplicate information by logically splitting the data.
- Ignoring SQL injection risks – Always validate inputs.
💡 Tip: Use the SQL Escape/Unescape tool to sanitize your data safely.
💬 What are common SQL errors beginners make? Forgetting syntax rules, mixing up WHERE vs. HAVING, and not checking data types are common beginner mistakes.
Advanced SQL: Beyond the Basics
Once you master the essentials, explore:
- Aggregate functions (
SUM(),COUNT(),AVG()) GROUP BYandORDER BYfor structured analysis- Subqueries and views for reusable data logic
- Stored procedures for automation
💬 What’s the difference between basic and advanced SQL? Basic SQL focuses on retrieving data, while advanced SQL enables you to analyze, optimize, and automate workflows.
SQL and the Future of Data
SQL remains the foundation of modern data science, analytics, and AI tools. Even as new technologies evolve, structured data remains the backbone of business decisions.
From marketing insights to AI-powered dashboards, SQL helps businesses make smarter, faster decisions every day.
💬 Will SQL still be important in the age of AI? Yes. SQL is evolving alongside AI — modern AI tools often use SQL queries behind the scenes to fetch and prepare data.
Master SQL to Unlock Data Confidence
Understanding what SQL is opens up endless possibilities for growth — both personally and professionally. With SQL, you can organize chaos into clarity, making better business and career decisions.
Start exploring SQL today with Microapp — your hub for digital productivity tools and learning resources.
✨ Tip: Practice small SQL challenges daily — consistency turns confusion into confidence!