Have you ever sold a product for $100 — but later realized you’re barely breaking even once expenses, taxes, and overhead are factored in? That’s where understanding your profit margin becomes crucial.
Profit margin tells you exactly what percentage of every dollar of revenue ends up as profit.
Whether you’re running a startup, a small business, or an enterprise, mastering profit margin calculation helps you price products and services more effectively, manage cash flow, and attract investors.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through:
- Every type of profit margin (gross, operating, EBITDA, net)
- Step-by-step profit margin formulas and examples
- How to calculate your selling price or cost from the margin
- Tips to boost your profit margins using proven strategies
- Access to our free profit margin calculator tool
What Is Profit Margin?
Profit margin measures how efficiently your business turns revenue into profit, or how much of every dollar earned you actually keep after covering your costs. It’s one of the most important profitability metrics for evaluating financial health and pricing strategy.
Here’s the basic profit margin formula:
Profit Margin = (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100
For example, if your business generates $10,000 in sales and your net profit (after all expenses) is $2,000, the calculation is:
(2,000 ÷ 10,000) × 100 = 20%
This means your profit margin is 20%, or that you keep $0.20 for every dollar of revenue after covering costs.
Profit margins can vary widely by industry. For instance, a software startup might have a 60% margin, while a retail store may operate closer to 10–15%. Understanding your profit margin helps you:
- Evaluate how efficiently your business operates.
- Identify areas to cut costs or improve pricing.
- Compare your performance against competitors.
- Set financial goals and plan for sustainable growth.
Put simply, the higher your profit margin, the more money your business retains from each sale, which means stronger pricing power, healthier cash flow, and better long-term stability.
Margin vs Markup: Don’t Get It Wrong
Many business owners confuse margin and markup, but they’re not the same.
| Term | Formula | Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Margin | (Profit ÷ Selling Price) × 100 | % of selling price kept as profit |
| Markup | (Profit ÷ Cost) × 100 | % added to the cost to reach the selling price |
Example:
If something costs $60 and you sell it for $100:
- Markup = (100−60)/60 = 66.7%
- Margin = (100−60)/100 = 40%
💡 Use margin when you want to measure profitability; use markup when setting prices.
Types of Profit Margin (with Formulas & Examples)
| Margin Type | Formula | What It Tells You |
|---|---|---|
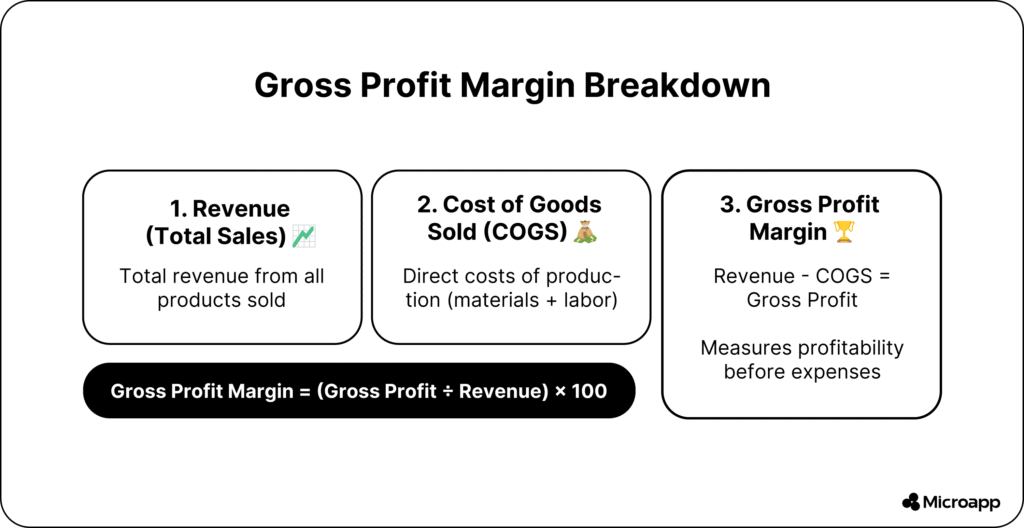
| Gross Profit Margin | (Revenue − COGS) ÷ Revenue × 100 | Efficiency of production and pricing |
| Operating Profit Margin | Operating Income ÷ Revenue × 100 | Profit after operating expenses |
| EBITDA Margin | (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation & Amortization ÷ Revenue) × 100 | Operational profitability ignoring financing structure. |
| Pretax Margin (EBT) | (Earnings Before Tax ÷ Revenue) × 100 | Profit before tax obligations |
| Net Profit Margin | Net Income ÷ Revenue × 100 | Final profitability after all costs |
Example:
Let’s say your small business had:
- Revenue: $100,000
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $40,000
- Operating Expenses: $30,000
- Taxes: $5,000
Then:
- Gross Profit Margin = (100,000 − 40,000) ÷ 100,000 × 100 = 60%
- Operating Profit Margin = (100,000 − 40,000 − 30,000) ÷ 100,000 × 100 = 30%
- Net Profit Margin = (100,000 − 40,000 − 30,000 − 5,000) ÷ 100,000 × 100 = 25%
How to Calculate Each Profit Margin (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Gather Your Data
You’ll need your revenue, COGS, operating expenses, and taxes or interest.
Step 2: Apply the Right Formula
Use the appropriate profit margin formula for the analysis you’re doing (gross, operating, or net).
Step 3: Convert to a Percentage
Multiply the result by 100 to express it as a percentage.
How to Calculate Selling Price or Cost Price Using Margin
Sometimes, you know your desired margin but not what price to charge. Here’s how to reverse-engineer it 👇
1️⃣ Selling Price = Cost ÷ (1 − Margin%)
If your product costs $50 and you want a 40% margin:
$50 ÷ (1 − 0.4) = $83.33 selling price
2️⃣ Cost = Selling Price × (1 − Margin%)
If you sell an item for $83.33 at a 40% margin:
$83.33 × (1 − 0.4) = $50 cost
This is one of the most sought-after profit margin calculations, ensuring your pricing strategy is sustainable and profitable.
Try Our Free Profit Margin Calculator
Want to skip the math? Use our interactive calculator to compute your instantly:
- Gross, Operating, and Net Profit Margins
- Selling Price or Cost from Desired Margin
👉 Try the Profit Margin Calculator and explore The Best Tax Software
What Is a Good Profit Margin?
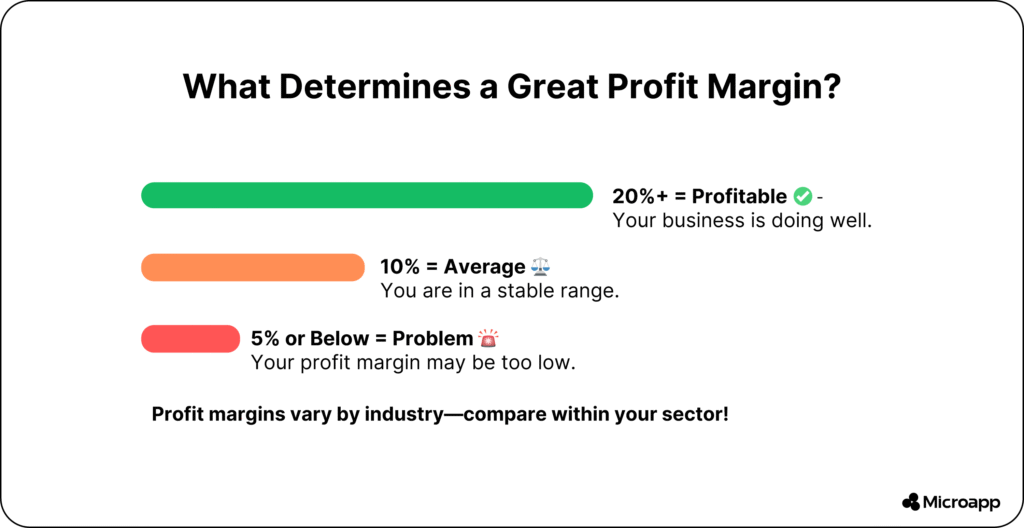
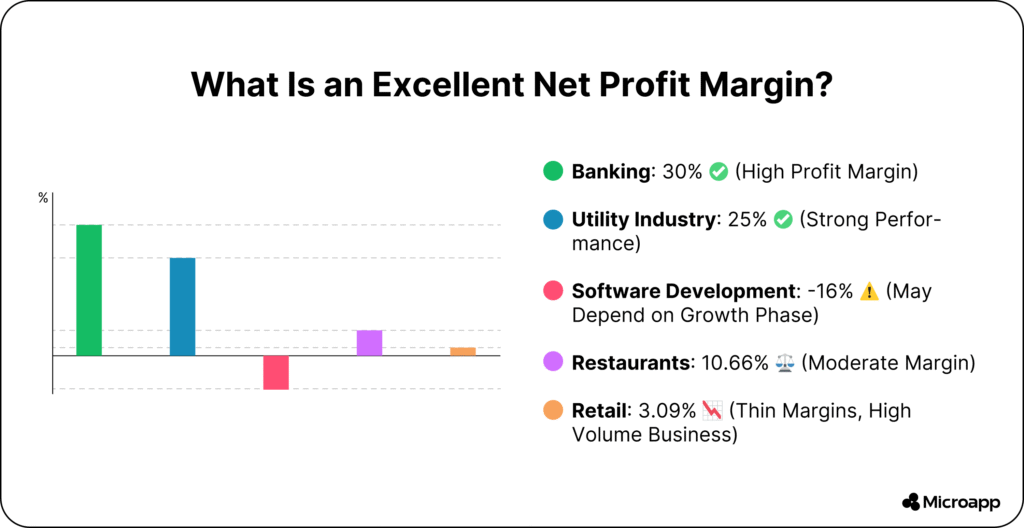
Good margins vary by industry. Here are some profit margin examples from 2024 studies:
| Industry | Average Net Profit Margin |
|---|---|
| Software / SaaS | 16–25% |
| Restaurants | 10–12% |
| Retail | 3–5% |
| Consulting / Agencies | 15–30% |
| Manufacturing | 8–12% |
👉 Tip: Compare your profit margins only with companies in your industry for meaningful insights.
Different Tools To Calculate Profit Margins
As shown here, we experimented with two techniques while calculating our profit margins.
Calculating Profit Margins With Our Tool
We found our tool to be easier to use, making it straightforward to calculate your profit margin. Follow these easy steps:
- Start by inputting your revenue by entering your total sales generated within a specific period.
- Next, you determine your COGS by calculating the direct costs of producing goods or services.
- Then consider your operating expenses, including all costs incurred in your business, such as utilities, marketing expenses, rent, and salaries.
- Consider your taxes and their implications for your profits.
- Lastly, you obtain your profit margin percentage, which the calculator calculates based on your input.
The best part is that our calculator can determine your present value, future value, number of periods, interest rate, and payment.
Calculating Profit Margin Using Excel
If you prefer computer software, you can calculate the gross profit margin within an Excel spreadsheet.
This process is lengthy, but still worthwhile. Before you start, you must add information on the cost of goods or services sold and revenue.
Here is a simple table with an explanation afterward:
|
A |
B |
C |
D | |
|
1 |
Revenue |
COGS |
Profit |
Profit Margin |
|
2 |
$100 |
$40 |
$60 |
60% |
|
3 |
$300 |
$75 |
$225 |
75% |
In column A, you add your revenue figure, followed by your COGS. Then, in column C, you input your formula to work out your prevailing profit.
So, once you add your figures to cells A2 and B2, the value in C2 will be the difference between A2 and B2. You will find the profit margin in column D. However, you must input your formula: (C2/A2) x 100.
Here is an example:
For the year ending December 31, 2024, Microapp recorded a revenue of 36,1 billion USD.
The operating income and gross profit are 9,7 billion USD and 5,1 billion USD. The net profit for the year is USD 3.8 billion. You will calculate your profit margins as follows:
- Gross profit margin = (9,7 billion USD ÷ 36,1 billion USD) × 100 = 28.9%
- Operating profit margin = (5,1 billion USD ÷ 36,1 billion USD) × 100 = 14.1%
- Net profit margin = (4,2 billion USD ÷ 29, 06 billion USD) × 100 = 11.6%
The example illustrates the importance of maintaining good operating and gross profit margins.
When a company has a deficiency at these levels, it loses money on operations, leaving it with less revenue to pay taxes and debt.
Still, the beneficial operating and gross profit margins enable Microapp to maintain a decent profit and meet all additional financial commitments.
Tips to Improve Your Profit Margins
✅ Track revenue and expenses carefully. Every unnecessary expense eats into your margin.
✅ Buy in bulk or negotiate supplier rates. Lower your COGS to increase gross margins.
✅ Automate and streamline operations. Software can reduce time and cost inefficiencies.
✅ Retain customers. It’s cheaper to sell again to existing clients than to acquire new ones.
✅ Focus on high-margin products. Discontinue or discount low-margin ones.
✅ Review pricing annually. Adjust for inflation and market demand.
Common Mistakes in Profit Margin Calculation
- Confusing markup with margin
- Ignoring overhead or fixed costs
- Comparing across unrelated industries
- Forgetting to include taxes or depreciation
- Using profit margin in isolation without a cash flow review
Calculating Profit Margins with Confidence
Profit margins help you measure how efficiently your business turns revenue into profit. By mastering the calculation of profit margin and understanding its various types, you can make more informed pricing, spending, and growth decisions.
Use the Profit Margin Calculator to get started instantly, or explore these related guides:
FAQs
What is profit margin in simple terms?
The profit margin indicates the percentage of sales revenue that remains after deducting expenses. It tells you how efficiently your business operates and how much profit you keep per sale.
How do you calculate profit margin?
You calculate the profit margin by dividing the profit by the revenue, then multiplying the result by 100. The formula is (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100.
What is a good profit margin?
A reasonable profit margin varies by industry but generally falls between 10% and 20% for most businesses. Higher margins usually indicate better cost control and stronger pricing power.
What’s the difference between gross profit margin and net profit margin?
Gross profit margin measures profit after direct production costs, while net profit margin includes all operating expenses and taxes. The net profit margin provides a clearer picture of overall profitability.
Why is profit margin significant for startups?
A profit margin helps startups understand whether their pricing and costs are sustainable. It’s key to attracting investors and ensuring long-term business growth.