APIs power nearly every modern app, connecting databases, services, and interfaces seamlessly. But a broken API can lead to slow apps, security issues, and frustrated users. That’s why API testing is essential.
API testing lets you catch bugs early, speed up feedback cycles, and decouple testing from the UI.
Whether you’re a QA engineer, developer, or tester, understanding API testing is essential to ensuring your applications remain reliable, secure, and scalable.
What is API Testing?
API testing is a type of software testing that examines an API to verify its functionality, reliability, performance, and security.
It ensures that your API endpoints behave as expected, return correct responses, and integrate seamlessly with other services.
FAQ: Why do we need API testing? Because APIs are the backbone of applications, any failure can break features, slow performance, or expose security vulnerabilities. API testing prevents these issues before they affect your users.
✍️ Tip: Treat API testing as the foundation of app reliability — start small, expand smart. Think of API testing as a safety net catching issues before they reach production.
Why API Testing Matters
API testing is critical because it solves real-world problems:
- Early bug detection – Catch issues before they reach production.
- Faster feedback – Integrates into CI/CD pipelines to provide instant results.
- Decoupling from UI – Test backend logic independently, reducing dependency on front-end readiness.
- Improved reliability & security – Ensures data integrity and prevents vulnerabilities.
FAQ: What problems does API testing solve? It detects functional and performance issues, prevents breaking changes, and helps maintain high-quality applications.
✍️ Tip: Prioritize testing for critical endpoints first to maximize impact.
Who Uses API Testing & When
- QA Engineers – Build automated test suites and validate API functionality.
- Developers – Ensure code changes don’t break endpoints.
- Testers – Perform integration, functional, and performance tests.
- When in the SDLC – API testing should start early during development and continue through CI/CD and production monitoring.
✍️ Tip: Shift left your API testing to catch issues sooner.
How API Testing Works – Step by Step
Before starting, you need:
- API specification and documentation
- Authentication and access credentials
- A dedicated test environment
Workflow:
- Send a request – Example:
GET /users/123 - Validate the response—check JSON fields, status codes, and headers.
- Chain requests – Test dependent sequences (e.g.,
POST /orders→ triggers inventory update.) - Automate tests – Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing.
- Monitor results – Track failures, analyze logs, and fix issues promptly.
FAQ: How do I start API testing? Start with a small set of critical endpoints, validate their responses, then expand coverage and automate as you go.
Tools like Microapp REST API Testing Tool simplify sending requests, validating responses, and monitoring performance.
✍️ Tip: Document each step and create reusable test templates.
Types of API Testing
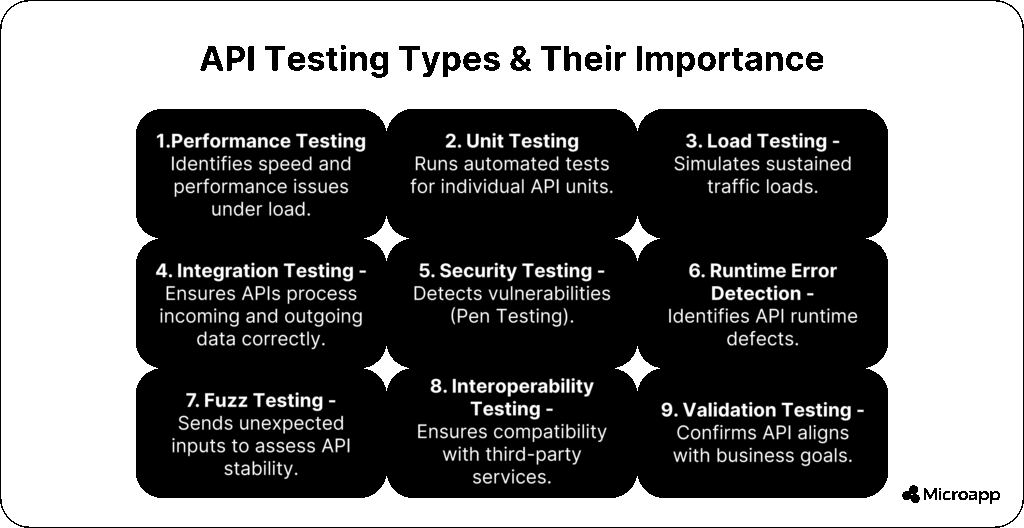
| Type of API Testing | Definition | Example | Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Tests individual endpoints in isolation. | Confirm POST /users creates a user correctly. | Unit tests catch simple logic errors early. |
| Integration Testing | Ensures multiple endpoints work together correctly. | POST /orders triggers inventory update and sends confirmation email. | Automate integration tests to reduce manual effort. |
| Functional Testing | Checks if APIs behave according to business rules. | GET /products returns only available items. | Combine functional tests with regression testing for reliability. |
| Contract Testing | Validates that API responses follow agreed formats. | JSON structure stays consistent across versions. | Contract tests prevent breaking changes for clients. |
| Performance / Load / Stress Testing | Measures speed, stability, and scalability. | Simulate 1,000 concurrent requests to GET /users. | Identify bottlenecks before production release. |
| Security Testing | Test the login endpoint against brute-force attacks. | Test the login endpoint against brute-force attacks. | Include security tests in your CI/CD pipeline. |
| Documentation / Interoperability / Reliability / Regression | Checks for vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and broken authentication. | N/A | Ensures documentation is correct, systems interact correctly, APIs are reliable under load, and updates don’t break existing functionality. |
FAQ: Why are multiple types of API testing important? Because each type addresses specific risks, combining them ensures comprehensive coverage and reduces production failures.
API Testing Tools & Technologies – 2025 Update
Choose tools based on protocol support (REST, SOAP, GraphQL, gRPC), automation capabilities, and CI/CD integration.
Tool Best For Highlights Microapp REST API Testing Tool Beginner to advanced Easy setup, automation ready, integrated reporting Postman API exploration & automation Collection-based testing, scripts for validation SoapUI / ReadyAPI SOAP and REST Functional & security testing, advanced assertions REST-assured Java automation Integrates into CI/CD pipelines JMeter Performance/load testing Simulate large traffic efficiently
FAQ: Which API testing tools are best for beginners? Tools like Microapp REST API Testing Tool and Postman allow you to start quickly without a complex setup.
✍️ Tip: Start with one tool that fits your workflow and scale as your testing needs grow.
Real-World Examples
REST API Example: GET /users
- Send a GET request.
- Validate status code
200 OK. - Check response fields (
id,name,email). - Measure response time (<500ms).
GraphQL / Microservices Example: Validate that queries and mutations return expected data and that they respect access controls.
FAQ: How do we test GraphQL or SOAP APIs differently? GraphQL requires validating queries and dynamic responses; SOAP requires XML validation and schema compliance.
✍️ Tip: Include security and contract tests for critical endpoints.
Best Practices for API Testing
| Best Practice | Details / Actionable Steps | Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Use a Dedicated Test Environment | Run tests in an isolated environment separate from production. Use staging or sandbox APIs to simulate real-world scenarios without risk. | Set up separate databases and endpoints for reliable testing. |
| Automate Tests & Integrate with CI/CD | Automate API tests to save time, reduce errors, and ensure consistent coverage. Trigger tests automatically on code commits or deployments. | Start automating critical endpoints first, then gradually expand coverage. |
| Use Meaningful Test Data & Mock Dependencies | Include realistic, edge-case, and invalid data—mock external services to isolate testing. | Mocking reduces test flakiness and enables testing scenarios that are difficult to reproduce in production. |
| Cover Functional & Non-Functional Testing | Test functionality, performance, load, stress, and security. Ensure APIs behave correctly under all conditions. | Include stress/load tests to catch bottlenecks before production. |
| Version Control & Contract Testing | Track API tests alongside code. Validate API responses follow agreed contracts to prevent breaking client applications. | Contract tests with every API update. |
| Maintain Documentation & Schema Validation | Keep API specifications and test cases updated. Validate response schemas to ensure consistency. | Update docs whenever endpoints change or new features are added. |
| Use Assertions on Status Codes, Headers, Body, & Performance | Validate all aspects of API responses, including success/failure codes, headers, payload data, and response times. | Include negative test cases to ensure proper error handling. |
| Keep Tests Maintainable & Readable | Write modular, reusable tests with clear naming conventions. Avoid hardcoding values. | Use descriptive test names so the team can understand the purpose at a glance. |
| Monitor APIs in Production | Testing in pre-production is essential, but monitoring APIs in real-world conditions is essential to detect hidden issues. | Set alerts for response times, error rates, and unexpected changes to the payload. |
| Continuously Review & Update Tests | Regularly review tests to cover new endpoints, updated requirements, and retire obsolete tests. | Schedule periodic audits to maintain comprehensive test coverage. |
Common Challenges & Pitfalls
- Incomplete test coverage → missed bugs
- Ignoring performance/security tests
- Brittle automated tests → frequent false failures
- Poor environment management → false positives/negatives
- Confusing UI vs API testing → missing more profound logic
FAQ: What are the common mistakes in API testing? Missing edge cases, ignoring performance/security, and failing to automate are the most frequent pitfalls.
✍️ Tip: Regularly review and update your tests to avoid these pitfalls.
Advanced Topics / Emerging Trends
- GraphQL & gRPC testing – dynamic queries and distributed data.
- Microservices architecture – end-to-end integration is crucial.
- AI/ML automation – auto-generates tests and detects anomalies.
- Shift-left testing & chaos engineering – simulate failures early.
- Cloud/SaaS API security – robust authentication and monitoring.
✍️ Tip: Stay updated with emerging trends to future-proof your API testing.
Start Testing Your APIs Confidently
API testing ensures your applications are reliable, secure, and high-performing.
By understanding the types, using the right tools, following best practices, and testing early, you reduce bugs, protect users, and accelerate development.
Start today with the Microapp REST API Testing Tool to automate and simplify your API tests. Learn more about how to streamline API testing and REST API automation testing.
Integrate API testing into your workflow — your users and team will thank you.