Do you know why every image counts? Images bring your website and digital content to life, but they also slow things down when not optimized.
Large, uncompressed files can hurt your page speed, frustrate users, and lower your Google ranking.
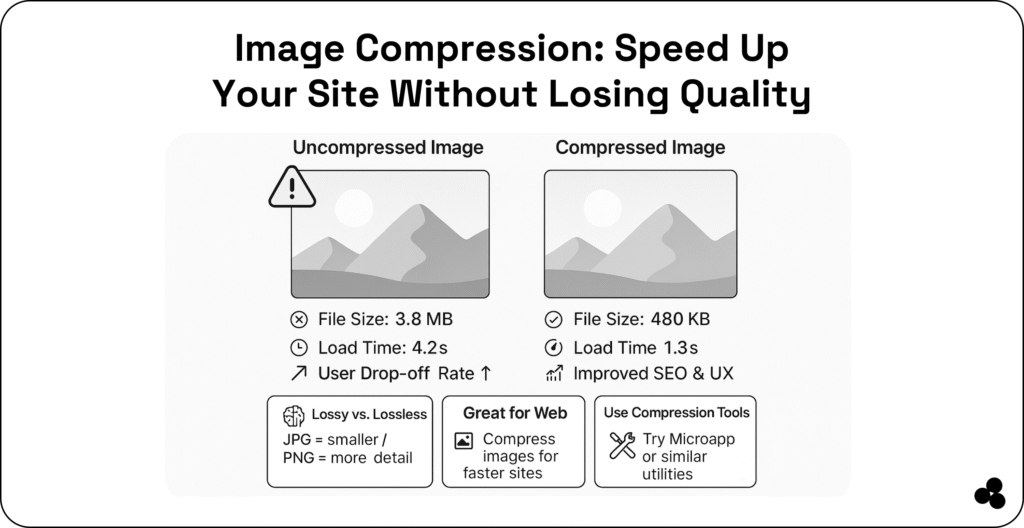
That’s where image compression comes in. It’s the process of reducing file sizes while maintaining crisp and clear visuals.
In this guide, you’ll learn exactly what image compression is, why it matters, and how to use it effectively to boost performance.
What is Image Compression?
Image compression is a technique that reduces the file size of an image without drastically affecting its visual quality. It removes redundant or non-essential data, allowing your files to take up less space.
What happens if you don’t compress images before uploading? If your pictures are too large, your pages load more slowly—especially on mobile—and users may leave before your content even appears.
Think of it like packing for a trip: compression lets you fit the same essentials into a smaller bag.
Example: A 5 MB image can often be compressed to 500 KB—with minimal loss of quality.
🔗 Try it yourself with the Microapp Image Compressor and see how much space you can save.
💾 Is image compression the same as resizing? Not quite. Resizing changes dimensions, while compression focuses on reducing file size while maintaining visual quality.
Why Image Compression Matters
When it comes to your website, you want one that is visually appealing, but it must also load quickly to keep your visitors engaged.
1. Faster Website Load Times
Page speed has a direct impact on both your SEO rankings and user experience. Compressed images make pages load faster, keeping users engaged and reducing bounce rates.
Check your site’s performance using Google PageSpeed Insights.
2. Save Storage and Bandwidth
Smaller files use less server space and data. That means faster backups, lower hosting costs, and improved scalability.
3. Mobile Optimization
Compressed images are vital for mobile-first websites. They load quickly, even on slower connections, and help your site meet Google’s mobile-first indexing standards.
💾 Does image compression affect SEO? Yes. Google rewards faster sites. Image compression is a crucial factor in enhancing Core Web Vitals and overall user experience.
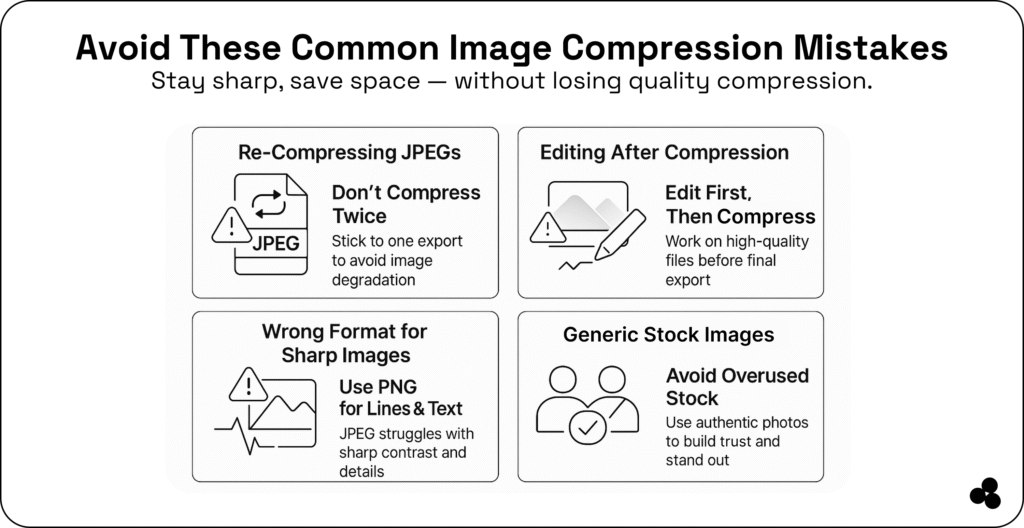
How Image Compression Works
Image compression works by reducing data in ways that the human eye can’t easily detect. There are two main types:
| Type | Description | Example Formats | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lossy | Removes data permanently for smaller file sizes | JPEG, WebP | Web images, blogs, social media |
| Lossless | Retains all original data | PNG, SVG | Logos, graphics, transparent backgrounds |
Example:
When compressing a JPEG, the algorithm reduces repetitive color data, saving space while maintaining the picture’s natural appearance.
💾 Which is better, lossy or lossless compression? It depends. Use lossy compression for photos or web graphics, and lossless compression for design files, logos, or any other content that requires perfect quality.
Modern frameworks, such as React and Tailwind CSS, make it easy to integrate optimized images directly into your workflow.
If you’re new to combining these technologies, check out How to Create a React and Tailwind App for a step-by-step approach.
Popular Image Formats Explained
1. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
Best for: Photographs, blog images, and e-commerce product pictures.
JPEGs use lossy compression, which slightly reduces image quality but saves a significant amount of space.
📸 Example:
A 5 MB high-resolution landscape photo can be compressed to just 500 KB as a JPEG — still perfect for your blog or portfolio site.
💡 Tip: Use JPEG for rich, colorful images that don’t need transparency.
2. PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
Best for: Logos, icons, and images requiring transparency.
PNG files use lossless compression, meaning no quality loss—but they’re usually larger than JPEGs.
📸 Example:
A company logo with a transparent background—such as one you’d overlay on a hero banner—should be saved as a PNG to maintain its sharp edges and transparent background.
💡 Tip: Combine optimized PNGs with CSS animations for a sleek, modern effect — check out CSS Transform Properties to learn how.
3. SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
Best for: Icons, infographics, and illustrations that require scaling without compromising quality.
SVGs are vector-based, meaning they use mathematical paths instead of pixels, keeping them sharp at any size.
📸 Example:
Your brand icon or navigation symbols on a responsive site can be SVGs — they’ll stay crisp on any screen size or device.
💡 Tip: Learn how to make the most of SVGs in The Benefits of Using SVG, pros and cons of SVGs, or see how to Convert SVG Files.
4. WebP (Web Picture Format)
Best for: Websites that need high performance without sacrificing quality.
Developed by Google, WebP uses both lossy and lossless compression, often cutting file sizes by 30–50% compared to JPEG or PNG.
📸 Example:
A hero image that’s 1 MB as a JPEG might shrink to 300 KB as WebP—with almost no visible difference.
💡 Tip: Check your site’s compatibility and load speed with Google PageSpeed Insights before switching formats.
5. GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
Best for: Simple animations or memes.
GIFs utilize lossless compression but are limited to 256 colors, making them unsuitable for complex visual content.
📸 Example:
Short looping animations, such as “loading” icons or funny memes, are ideal as GIFs—but don’t overuse them; they can slow down pages.
💡 Tip: If you use GIFs, compress them first with tools like Microapp Image Compressor to keep your site fast.
Benefits of Image Compression
- Boosts Performance – Improves loading time and user experience.
- Improves SEO – Faster sites rank higher on Google.
- Reduces Bounce Rate – Keeps users from leaving due to slow load times.
- Saves Costs – Requires less bandwidth and server space.
- Eco-Friendly – Lower data transmission means less energy consumption.
💾 How does image compression help mobile users? Compressed images load quickly, even with low connectivity—making your content more accessible globally.
How to Implement Image Compression
- Compress before uploading: Always optimize before adding images to your CMS.
- Use AI-based tools: Save time by letting automation handle optimization.
- Regularly check your performance by testing with PageSpeed Insights.
- Balance quality and speed: Test your images on multiple devices to ensure optimal performance.
💾 Can AI automate image compression? Absolutely. AI-powered tools can detect image types, analyze visual data, and automatically apply the most suitable compression methods.
Compress Smarter, Not Harder
Image compression isn’t just a technical process; it’s a strategic advantage. Faster websites, happier visitors, better SEO—it all starts with smaller, smarter images.
Take control of your performance today with Microapp — and start optimizing your digital assets like a pro.